System Overview
-
GPS
- Operated by the United States Air Force.
- Global coverage available since April 1995.
- Space segment includes 32 satellites arranged into 6 orbital planes, each with a minimum of 4 satellites.
- Satellties Orbit the Earth at an inclination of 55° and an altitude of 12,550 miles (20,200 km).
- Each satellite circles the Earth once every 11 hours and 58 minutes.
- Transmits signals for civillian use over L1 (1575.42 MHz) and L5 (1176.45 MHz) bands.
- Provides a positional accuracy of 11.4 - 25.5 feet
(3.5 - 7.8 meters).
-
GLONASS
- Operated by the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces.
- Global coverage available since November 2011.
- Space segment includes 24 satellites arranged into 3 orbital planes, each with 8 evenly spaced satellites.
- Satellites orbit the Earth at an inclination of 64.8° and an altitude of 11,868 miles (19,100 km).
- Each satellites circles the Earth once every 11 hours and 15 minutes.
- Transmits signals for civillian use over L1 (1602 MHz) band only.
- Provides a positional accuracy of 16.4 - 32.8 feet
(5 - 10 meters).
-
Galileo
- Operated by the European GNSS Agency (GSA).
- Global coverage available since 2019.
- Space segment will include 30 satellites arranged into 3 orbital planes, each with 8 active and 2 spare satellites.
- Satellites orbit the Earth at an inclination of 56° and an altitude of 14,429 miles (23,222 km).
- Each satellites circles the Earth once every 14 hours and 7 minutes.
- Transmits signals for civillian use over E1 (1575.42 MHz) and E5a (1176.45 MHz) bands.
- Provides a positional accuracy of 6.5 - 9.8 feet (2 - 3 meters).
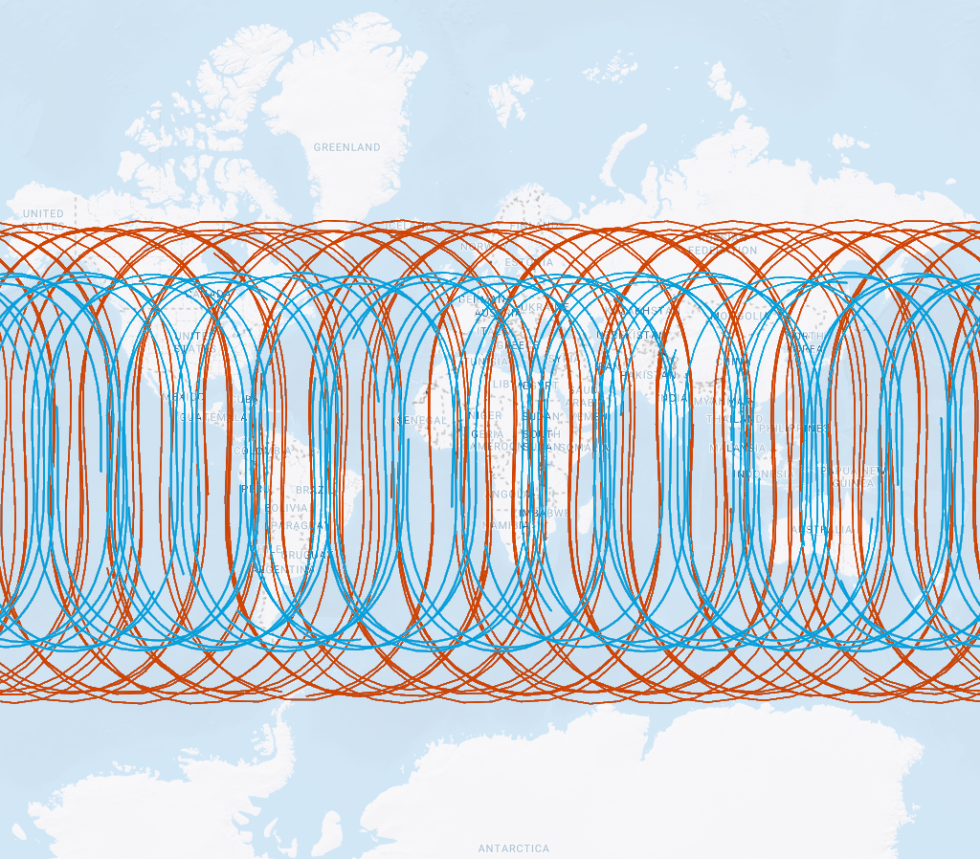
Constellation Geometry
- Earth Geometry
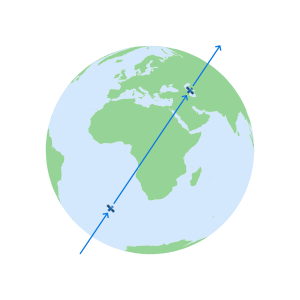
A view of the Earth
as seen from above
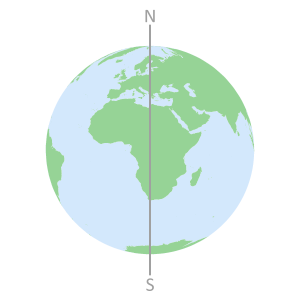
the continent of AfricaThe Earths rotational axis
intersects its surface at the
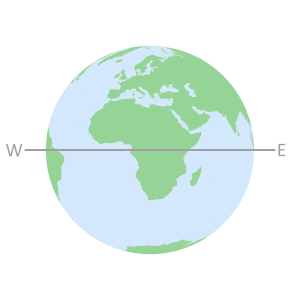
North and South polesThe Equator is perpendicular
to the rotational axis and
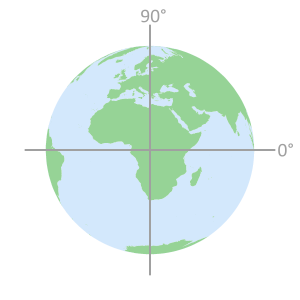
equidistant from the polesThe Inclination angle for
each GNSS constellation is
measured from the Equator
- GPS Geometery
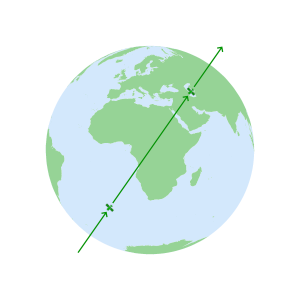
Satellites circle the Earth
in one of six orbital planesEach orbital plane
is indexed with an
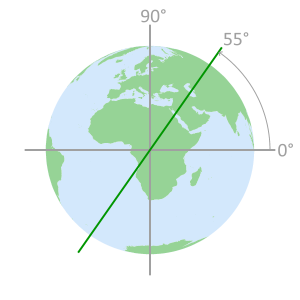
Inclination angle of 55°Constellation geometry
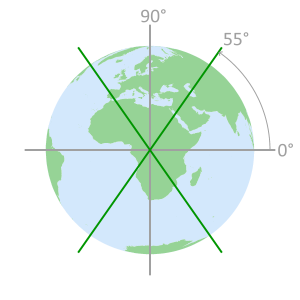
cross section displaying
orbital plane intersectionsSatellites do not pass
over the area inside the
remaining 35° of latitude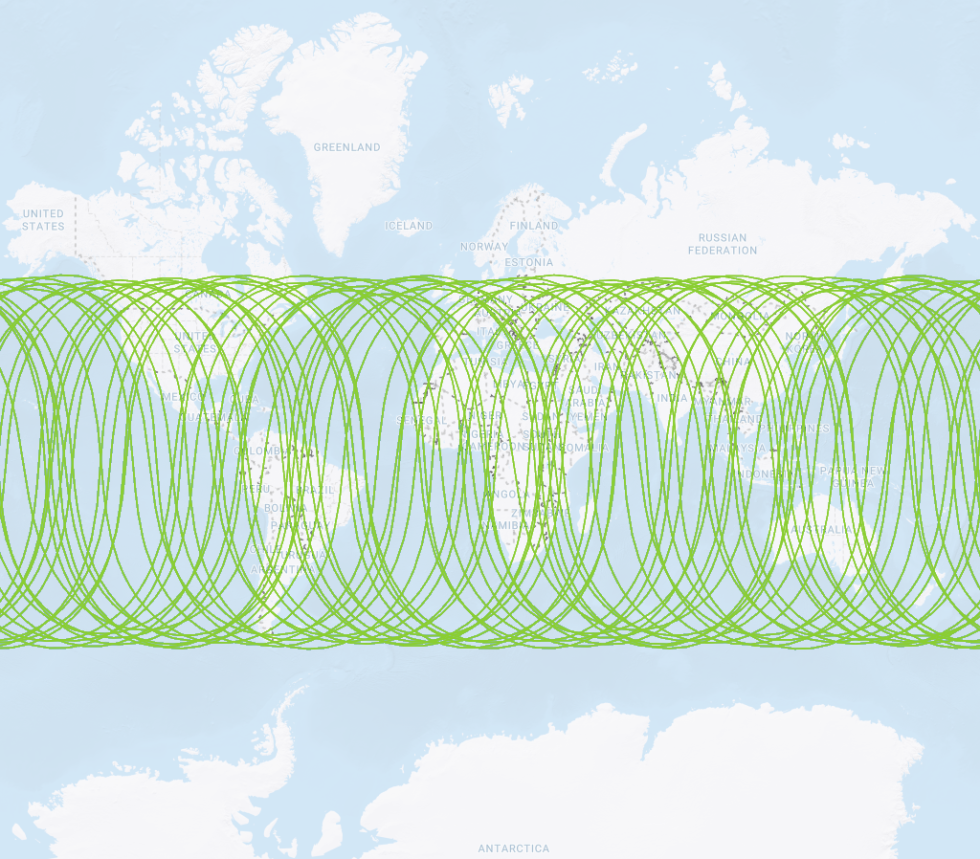
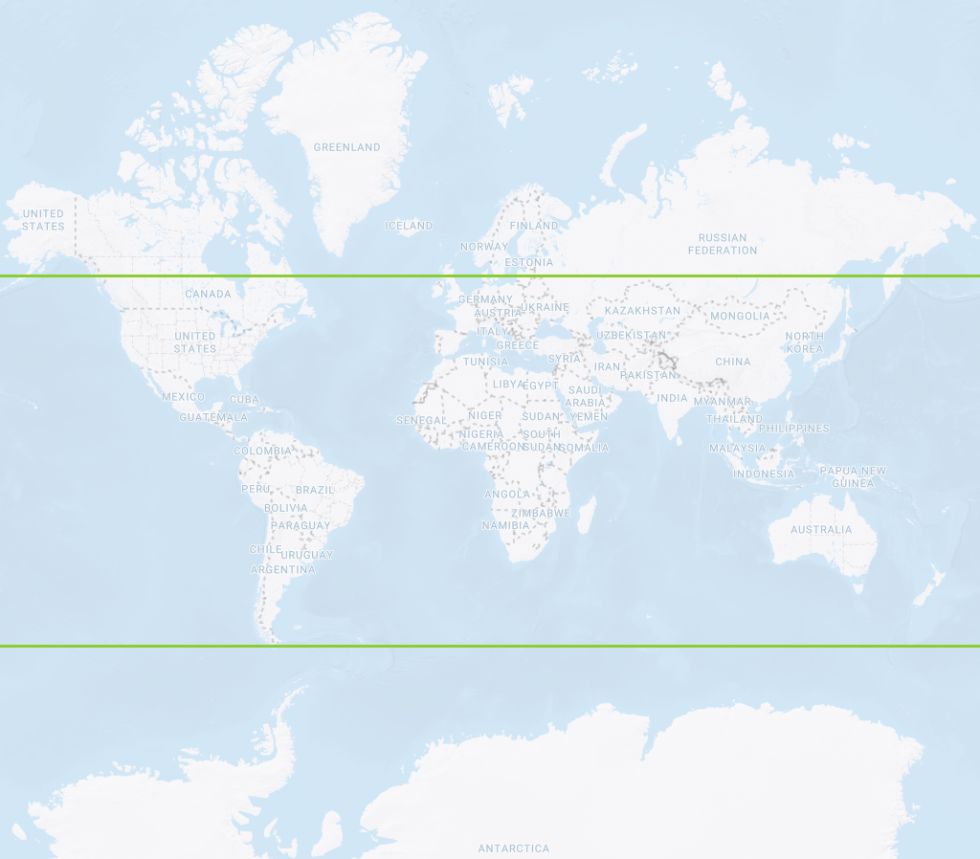
GPS satellite orbit paths GPS inclination angle orbit limits
- GLONASS Geometery
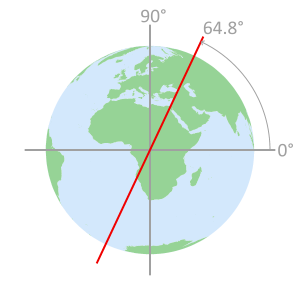
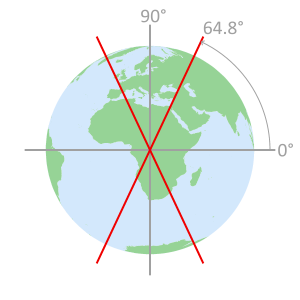
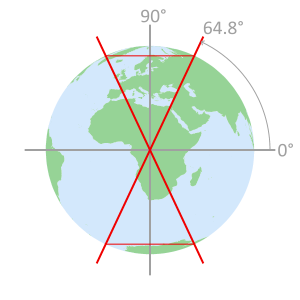
Satellites circle the Earth
in one of three orbital planesEach orbital plane
is indexed with an
Inclination angle of 64.8°Constellation geometry
cross section displaying
orbital plane intersectionsSatellites do not pass
over the area inside the
remaining 25.2° of latitude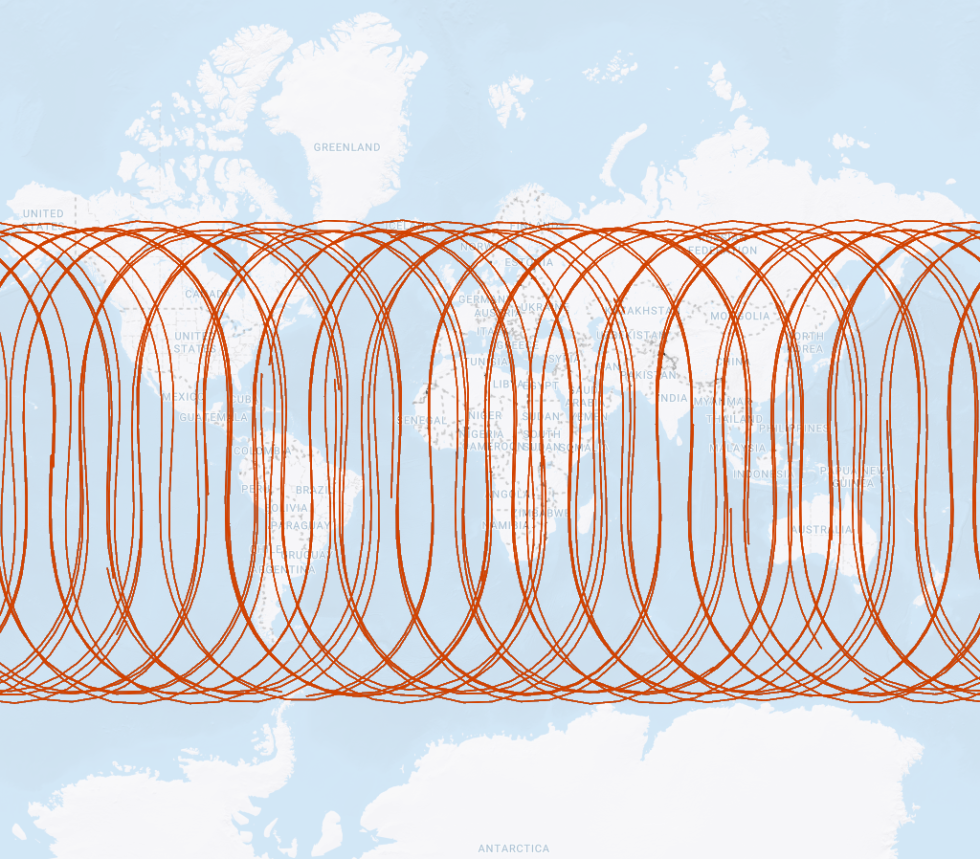
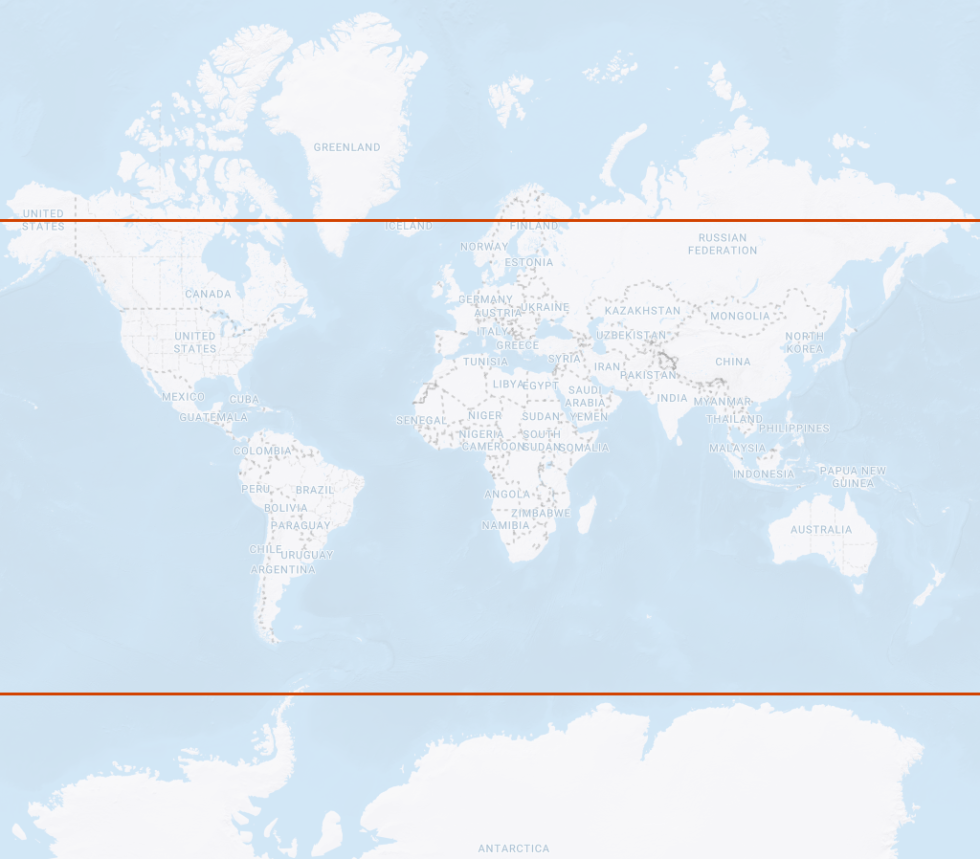
GLONASS satellite orbit paths GLONASS inclination angle orbit limits
- Galileo Geometry
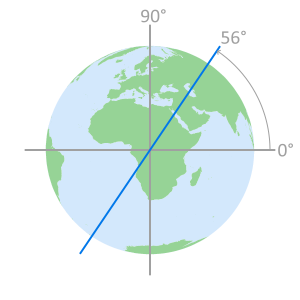
Satellites circle the Earth
in one of three orbital planesEach orbital plane
is indexed with an
Inclination angle of 56°Constellation geometry
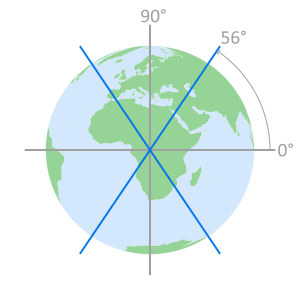
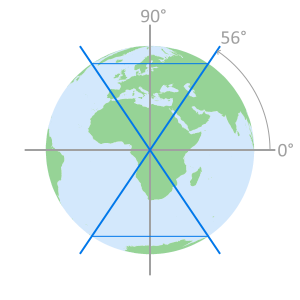
cross section displaying
orbital plane intersectionsSatellites do not pass
over the area inside the
remaining 34° of latitude
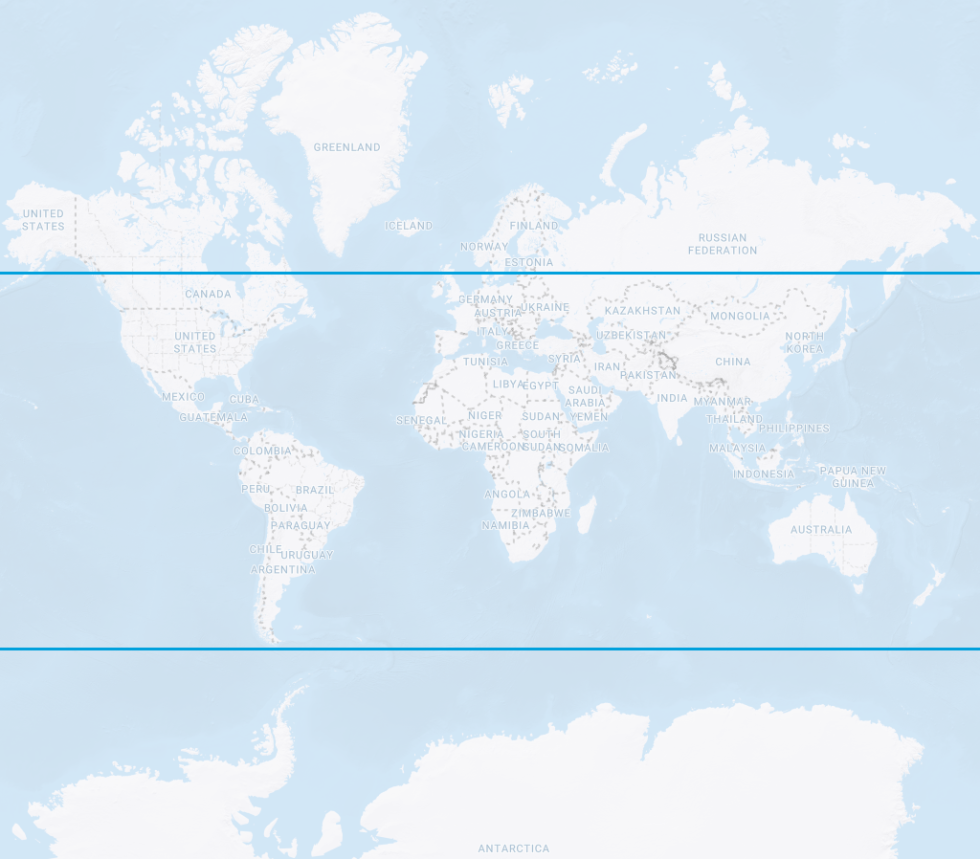
Galileo satellite orbit paths Galileo inclination angle orbit limits
Geometry Comparison
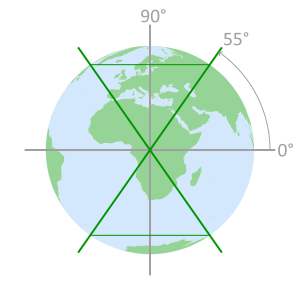
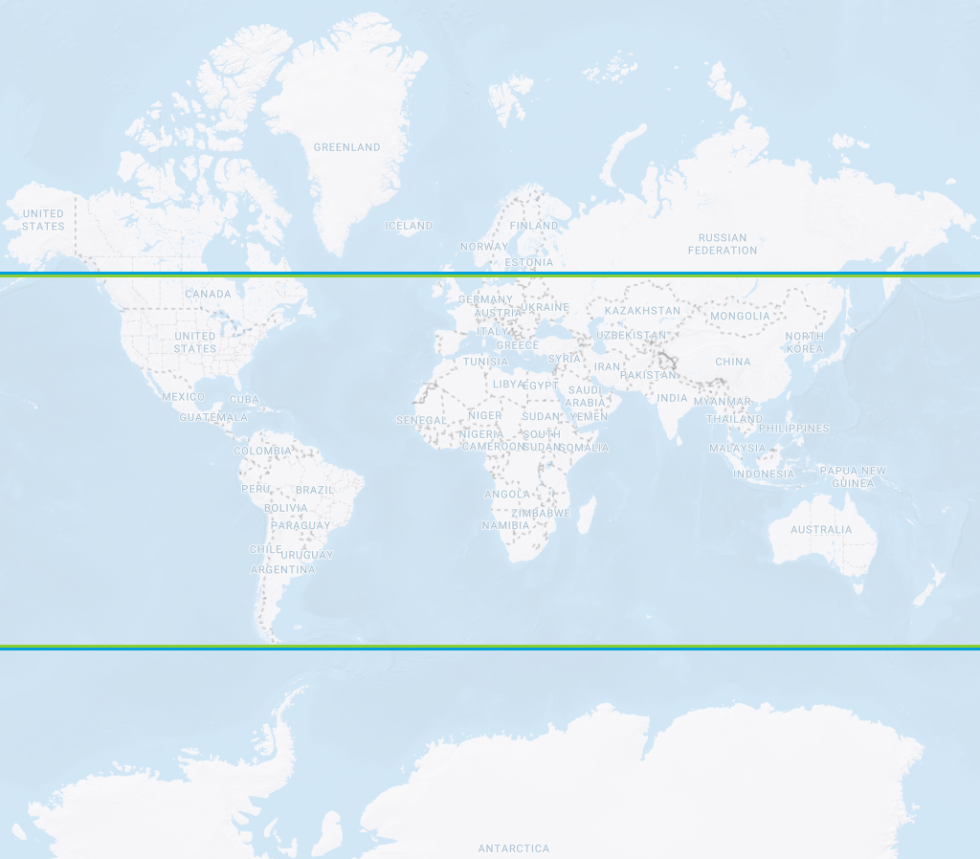
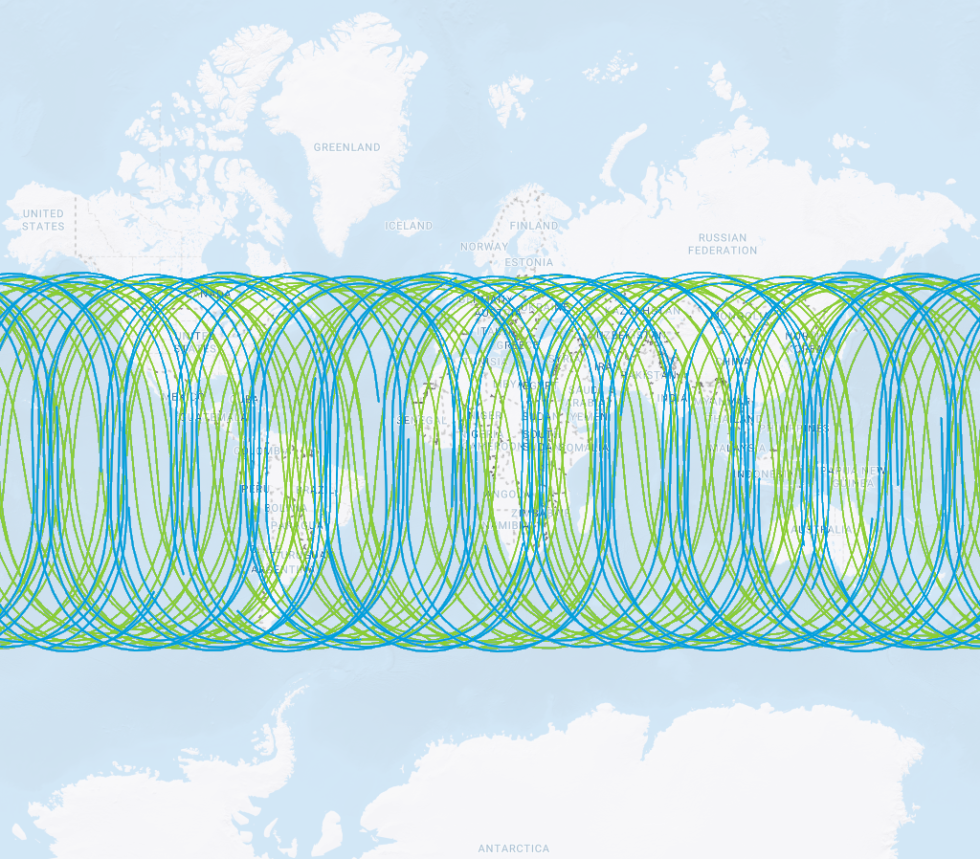
- GPS vs GLONASS
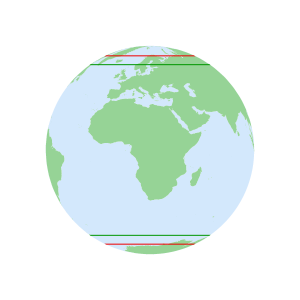

GPS vs GLONASS Inclination angle orbit limits Satellite orbit paths - GPS vs Galileo
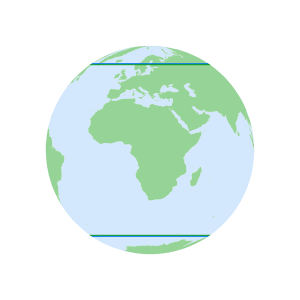
GPS vs Galileo Inclination angle orbit limits Satellite orbit paths - Galileo vs
GLONASS
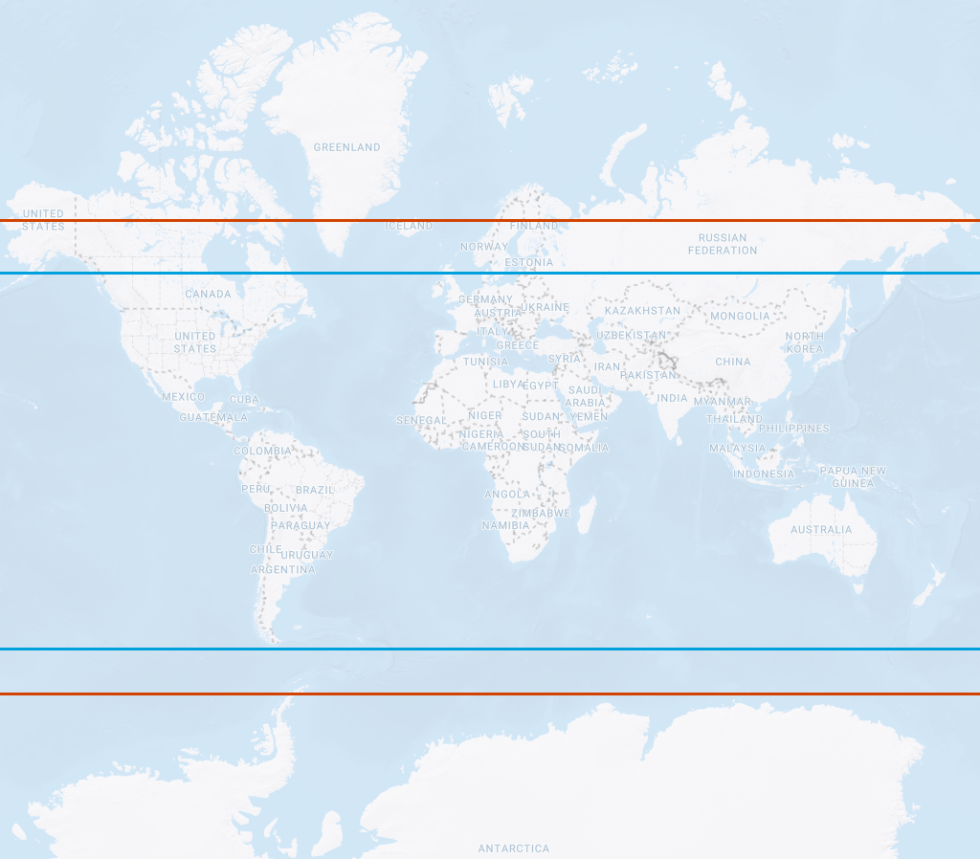
Galileo vs GLONASS Inclination angle orbit limits Satellite orbit paths
Position Calculation
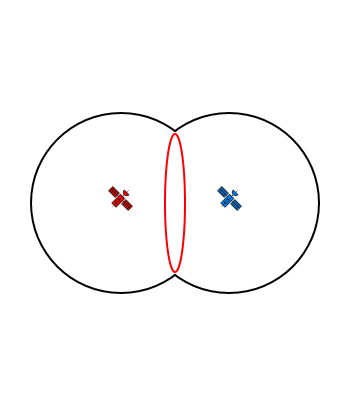
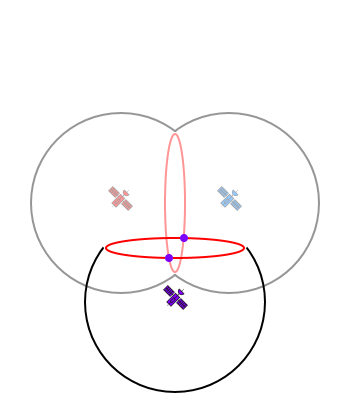
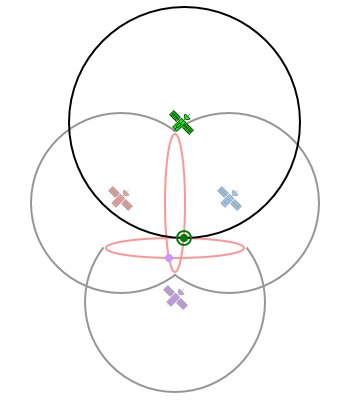
- Consumer grade GPSr require a minimum of four satellite signals before they can calculate their position using trilateration.
- One satellite is always reserved by the GPSr for the exclusive purpose of synchronizing all signals to a single atomic clock.
- Knowing the distance to three satellites enables the GPSr to determine two potential solutions (and then guess the correct one).
- An absolute location can be confidently calculated only when four (or more) distance values are available
 |
 |
 |
| The receiver is located somewhere along the intersection of two signals. |
Adding a third signal further isolates the solution to one of two possibilites. |
The true location is revealed only after a fourth signal is applied to the calculation. |
Satellite Selection
- The GPSr will use the satellites in the best
position for calculating your current location.
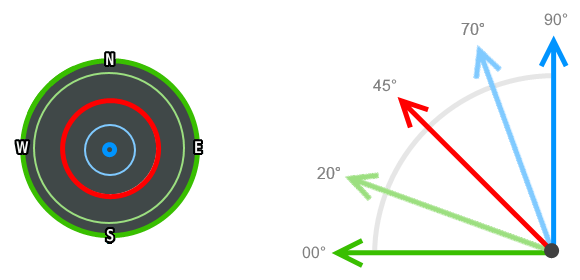
- Zenith: Satellites located overhead (70° - 90° elevation) are best suited for vertical position calculations (GPS Elevation).
- Inclination: Satellites visible midway in the sky (20° - 70° elevation) provide the best accuracy when calculating latitude and longitude.
- Horizon: Satellites near the horizon (0° - 20° elevation) are less reliable due to potential geographic and atmospheric intereference.
Satellite Visiblity
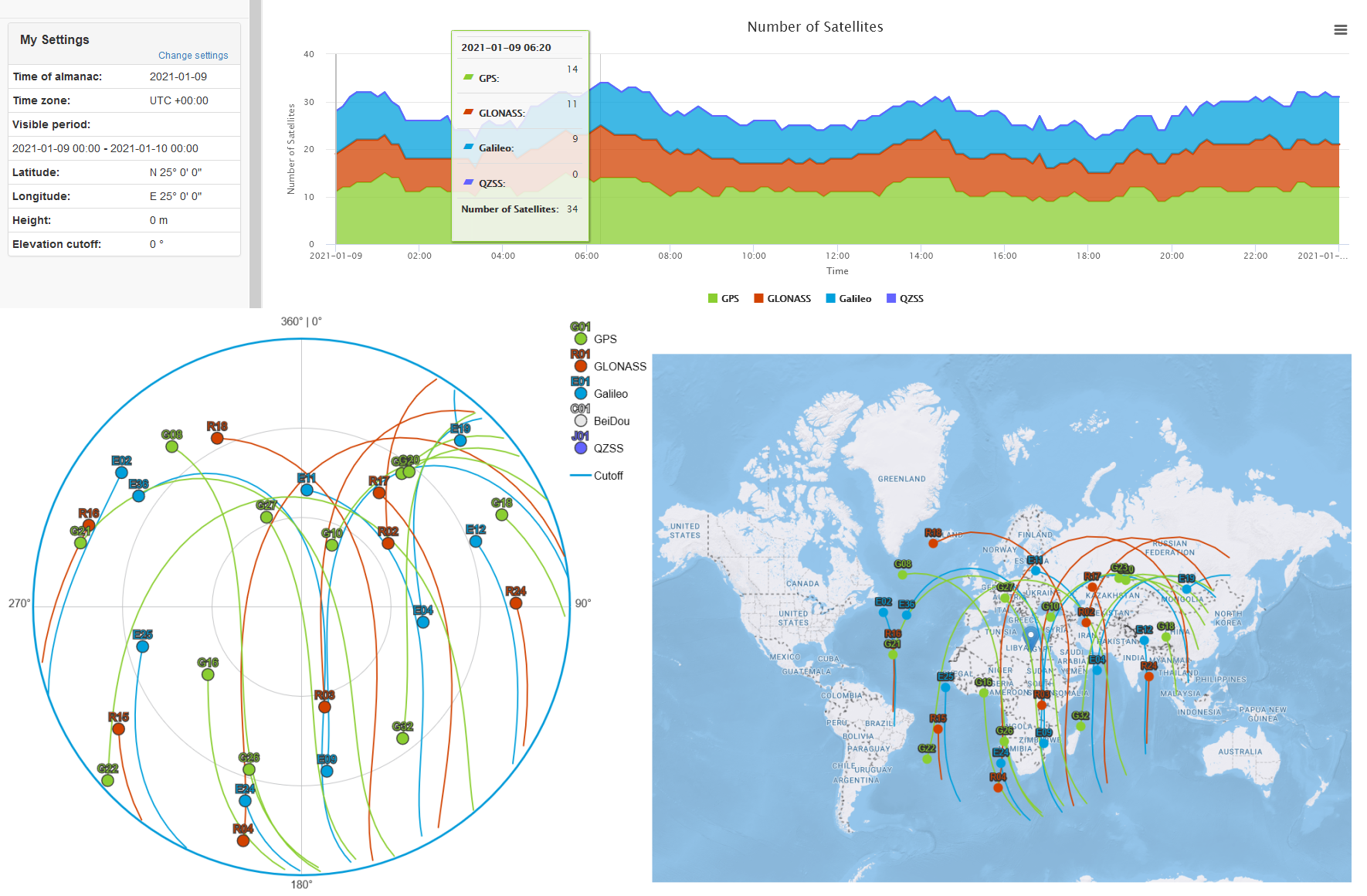
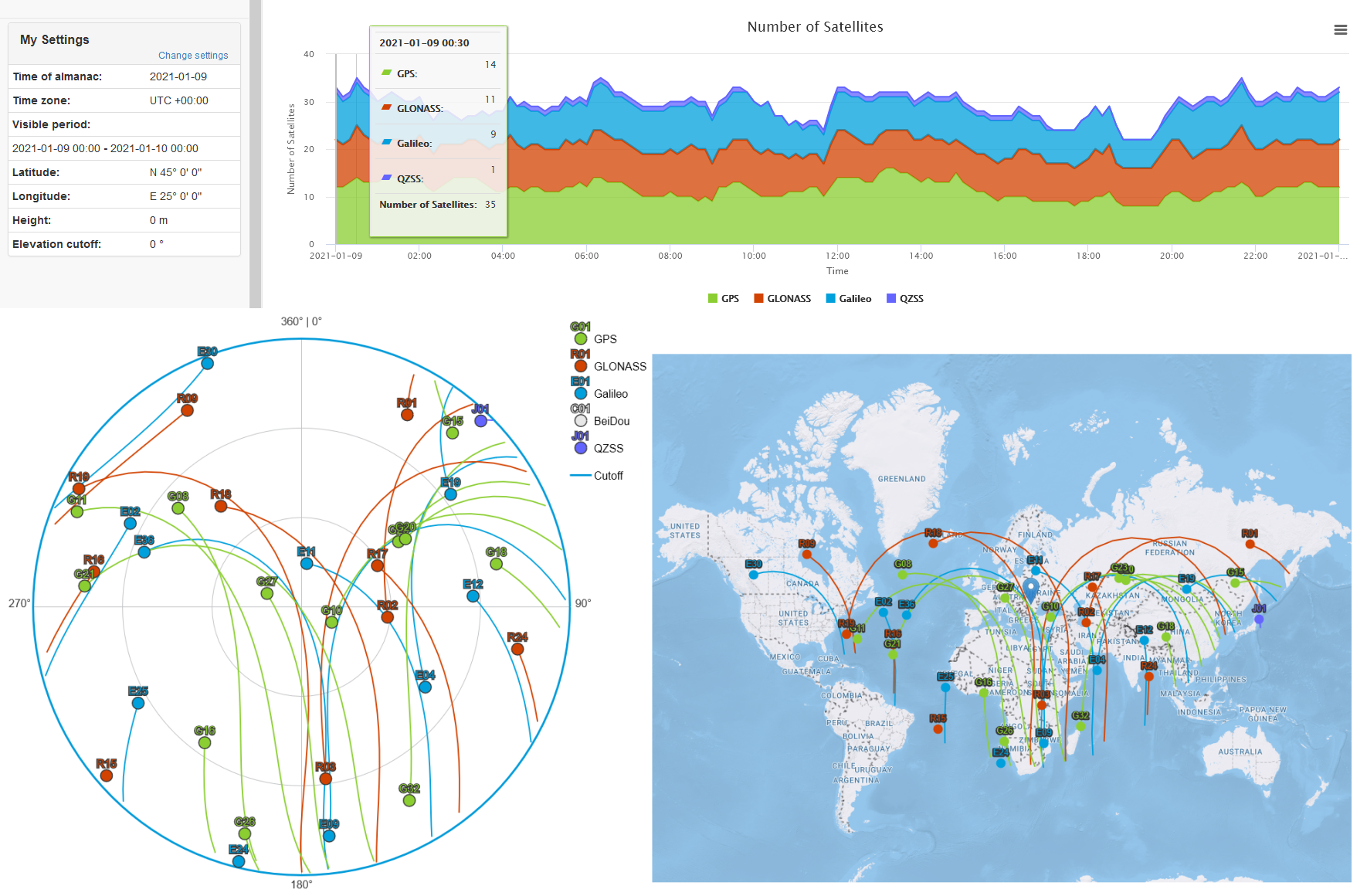
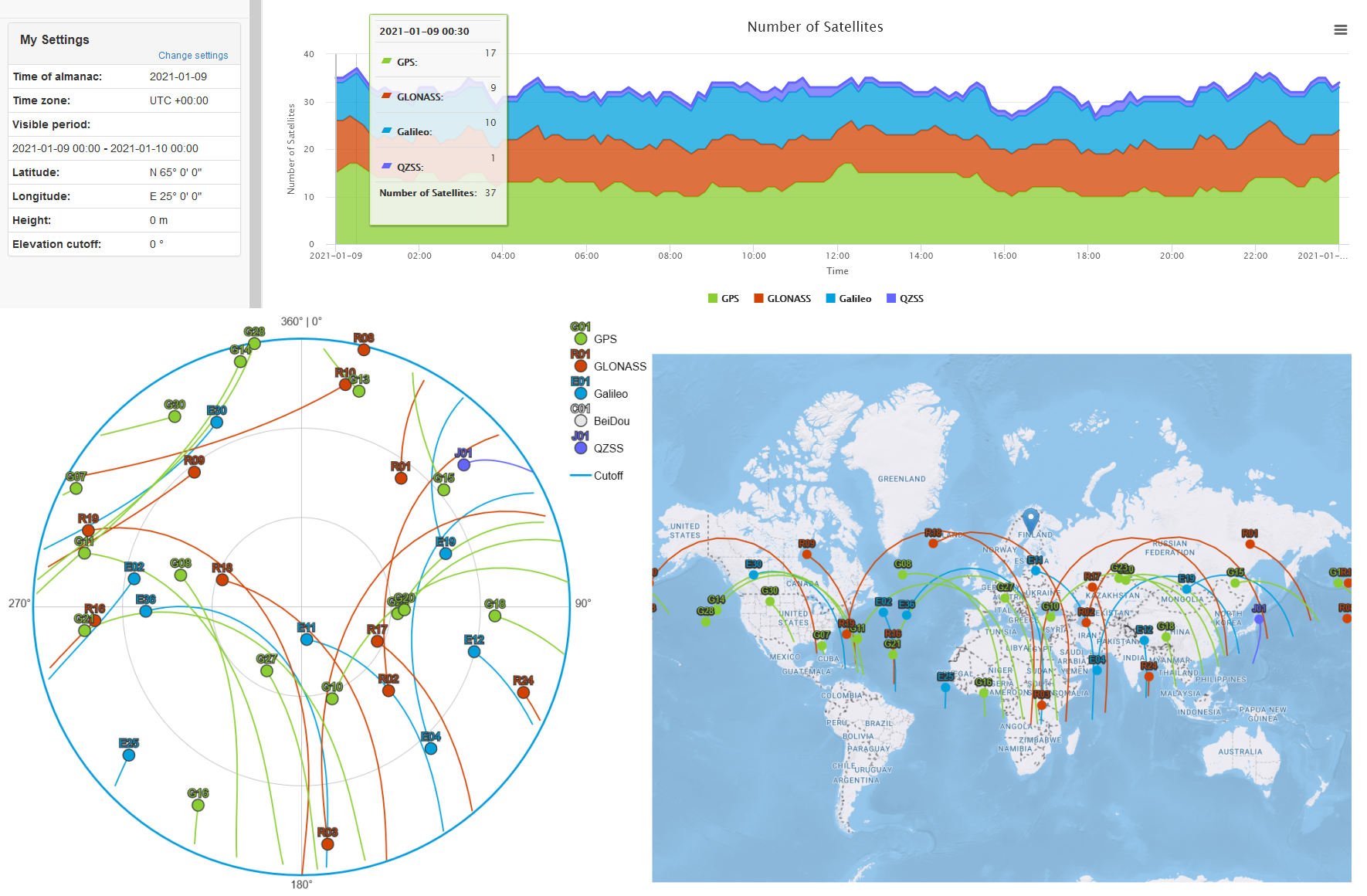
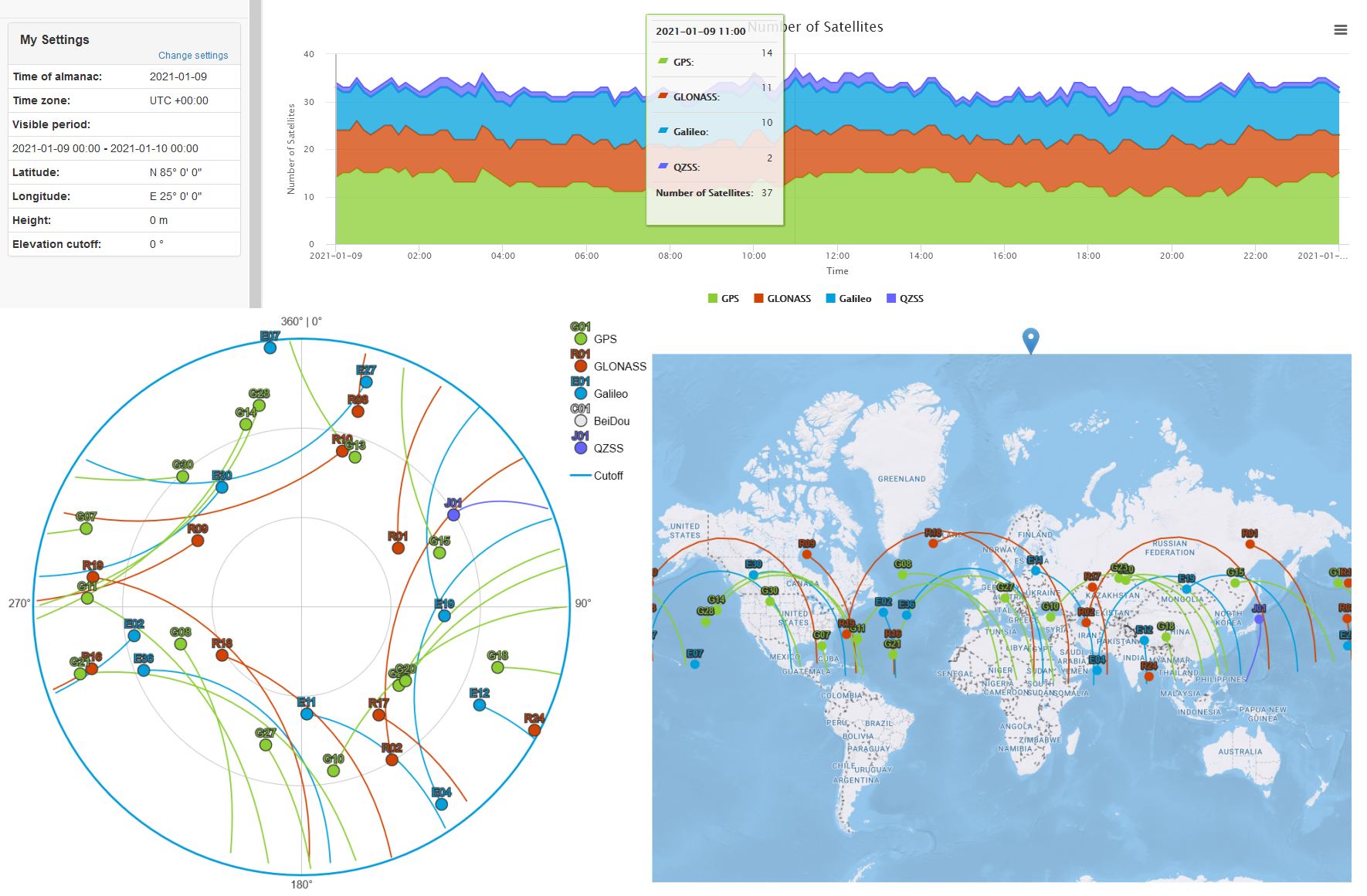
- Using a Satellite Visibility Prediction Service twe can determine which satellites will be visible for any given location, date and time.
- In the following example, we wanted to check GPS, GLONASS and Galileo satellite visibility from multiple latitudes in the northern hemisphere.
- Results were plotted over a 24 hour period for N 5°, N 25°, N 45°, N 65°, and N 85° latitude, all along E 25° longitude.
- While the number of visible satellites for each constellation fluctuated slightly, the sum of available satellites at each latitude did not vary significantly.
- GPS seemed to provide the best satellite availability, while GLONASS and Galileo maintained slightly lower and similar visibility levels.
- None of the charts indicated an insufficient number of total available satellites during the 24 hour test period.
- Choosing GPS + GLONASS or GPS + Galileo appeared to always yield a similar number of available satellites.
- The charts also revealed how the position of the satellites in the sky changes relative to the latitude from which they are observed.
- Fewer satellites were available directly overhead as the latitude increased, and were instead positioned at more favorable elevation angles that contribute to improved horizontal accuracy at the expense of GPS derived elevation calculations.
- Based on these observations, one can conclude that a dual-GNSS capable receiver would be a minimum requirement for relaible navigation at higher latitudes, where a Multi-GNSS and Multi-Band receiver is likely to offer the best performance.
- Satellite visibility
charts: